Wheezing, a high-pitched whistling sound, is a common indicator of chronic respiratory diseases, including asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), due to inflammation and swelling of the airways.
Early detection and management of asthma and COPD is critical. While digital stethoscopes are an improvement over traditional stethoscopes, they pick up airborne noise, which interferes with wheeze detection. An advanced technological solution is needed that could be used as a screening tool in the clinic and for remote patient monitoring, which would enable physicians to intervene early.
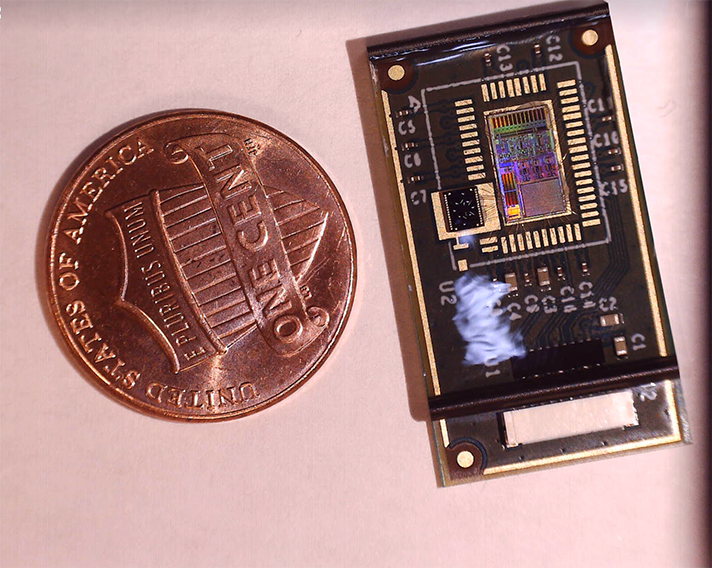
Researchers at the Georgia Institute of Technology have developed a deep learning model that they paired with a wearable patch equipped with a highly sensitive sensor that can automatically detect wheezing sounds. The deep learning model has the potential to classify respiratory diseases, which could speed up their diagnosis and treatment. The results of the pilot patient study were published in BioSensors.
